
The requirement for exploitation is a authentication. It is possible to initiate the attack remotely. It is possible to read the advisory at This vulnerability is uniquely identified as CVE-2014-0839 since. IBM Rational Focal Point 6.4.x and 6.5.x before 6.5.2.3 and 6.6.x before 6.6.1 allows remote authenticated users to modify data via vectors involving a direct object reference. This is going to have an impact on integrity. The manipulation with an unknown input leads to a access control vulnerability. A high score indicates an elevated risk to be targeted for this vulnerability.Ī vulnerability was found in IBM Rational Focal Point up to 6.5.2.0. The CTI Interest Score identifies the interest of attackers and the security community for this specific vulnerability in real-time. and 41: sites.Our Cyber Threat Intelligence team is monitoring different web sites, mailing lists, exploit markets and social media networks.and 37: Summary and next steps In this guid.and 35: If you consider Price to be much mo.and 25: What’s New The What’s New mode.
 and 23: Gantt The Gantt mode is useful when. and 21: Attribute statistics The Attribute. and 19: Displaying the elements Rational Fo. and 15: After you add the cars, you will ha. and 7: Creating a module of elements Creat. and 3: © Copyright IBM Corporation 1997. 1997, 2009 Getting Started with IBM® Rational® Focal Point 5(41) The screenshots in this guide are based on Rational Focal Point version 6.4.1. However, to complete these tasks, you do not have to use an empty workspace the module in the example can be created in any workspace. The example and screenshots in this document are based on a fresh workspace, with no other modules than the ones that are created automatically with a new workspace. You can use either an installed local version of the tool on your computer, or a hosted installation. Prerequisites To complete the tasks in this guide, you must be the administrator for a workspace in Rational Focal Point. 1997, 2009 Getting Started with IBM® Rational® Focal Point 4(41) For example, a view can be defined to display only elements that have a New status, or all elements that have been assigned to a certain user. For Rational Focal Point, a view is what the user is allowed to see a view normally contains only a subset of the information in the repository. Only administrators have access to the repository – normal users only see information through views that the administrator creates. View – A view is a way of displaying information that is stored in the repository (the modules). For example, the element Car 1 contains the attributes ID, Title, Description, Type, and Price. Attribute – All elements are composed of a set of attributes. For example, a module called Cars contains the elements Car 1, Car 2, Car 3, Car 4, Car 5, Car 6, and Car 7. Element – Each module contains elements. Build a module for each type of information, and use different modules for different levels of information. A module contains elements, and all elements within the same module share the same set of attributes. Different types of information are handled in different modules. Module – The repository in which you store all information is structured in a number of modules. To better understand the tasks in this guide, note these basic concepts:
and 23: Gantt The Gantt mode is useful when. and 21: Attribute statistics The Attribute. and 19: Displaying the elements Rational Fo. and 15: After you add the cars, you will ha. and 7: Creating a module of elements Creat. and 3: © Copyright IBM Corporation 1997. 1997, 2009 Getting Started with IBM® Rational® Focal Point 5(41) The screenshots in this guide are based on Rational Focal Point version 6.4.1. However, to complete these tasks, you do not have to use an empty workspace the module in the example can be created in any workspace. The example and screenshots in this document are based on a fresh workspace, with no other modules than the ones that are created automatically with a new workspace. You can use either an installed local version of the tool on your computer, or a hosted installation. Prerequisites To complete the tasks in this guide, you must be the administrator for a workspace in Rational Focal Point. 1997, 2009 Getting Started with IBM® Rational® Focal Point 4(41) For example, a view can be defined to display only elements that have a New status, or all elements that have been assigned to a certain user. For Rational Focal Point, a view is what the user is allowed to see a view normally contains only a subset of the information in the repository. Only administrators have access to the repository – normal users only see information through views that the administrator creates. View – A view is a way of displaying information that is stored in the repository (the modules). For example, the element Car 1 contains the attributes ID, Title, Description, Type, and Price. Attribute – All elements are composed of a set of attributes. For example, a module called Cars contains the elements Car 1, Car 2, Car 3, Car 4, Car 5, Car 6, and Car 7. Element – Each module contains elements. Build a module for each type of information, and use different modules for different levels of information. A module contains elements, and all elements within the same module share the same set of attributes. Different types of information are handled in different modules. Module – The repository in which you store all information is structured in a number of modules. To better understand the tasks in this guide, note these basic concepts: #Focalpoint ibm how to
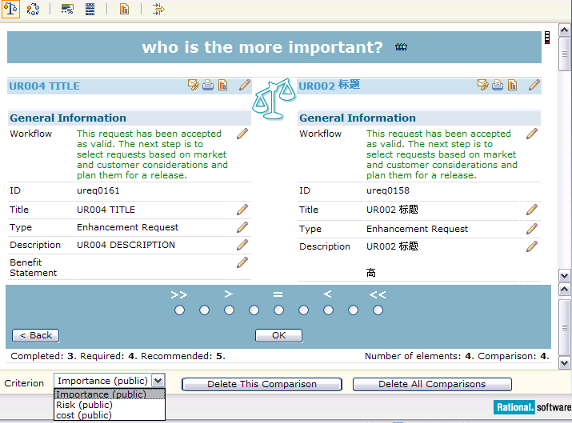
You can learn how to add a module that contains information about cars, add some cars, prioritize them according to design and cost, and then see which one is best according to certain criteria.
By following the Cars example in this guide, you can learn to use the basic decision-making features of the product and to analyze and draw conclusions from the results. Introduction This document is intended to guide you through a few basic tasks in IBM® Rational® Focal Point: from setting up a simple module, through prioritization and visualization, to printing.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
